A current asset which indicates the cost of the insurance contract (premiums) that have been paid in advance. It represents the amount that has been paid but has not yet expired as of the balance sheet date. A record in the general ledger that is used to collect and store similar information. For example, a company will have a Cash account in which every transaction involving cash is recorded. A company selling merchandise on credit will record these sales in a Sales account and in an Accounts Receivable account.

Single Economic Entity Concept Consolidation Accounting
It is a more complete and accurate alternative to single-entry accounting, which records transactions only once. Presented in alphabetical order, this glossary of accounting terms covers essential basics and key concepts. what are retained earnings You can look up individual terms, or read the guide from start to finish for a quick crash course in accounting fundamentals. Get insights into the types of accounting concepts with their meanings. Then, you can convert them into helpful accounting concepts in pdf or accounting concepts ppt for a quick overview of accounting concepts and standards.
Time Period
The realization concept states that the entity should record an asset at cost until and unless the realizable value of the asset has been realized. Practically, it will be correct to say that the entity will record the realized value of the asset once the asset has been sold or disposed of off, as the case may be. Below mentioned are the generally accepted accounting concepts used widely around the world. The matching principle states that expenses should be recognized in the same period as the revenue they help generate. This equation highlights the relationship between a company’s resources, debts, and owners’ claims.
Comparability / Consistency

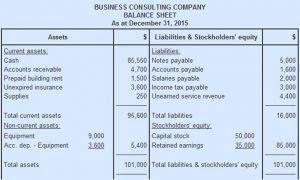
This blog post aims to demystify common accounting terms and concepts, providing you with a solid foundation to navigate the financial world. Journal entries usually dated the last day of the accounting period to bring the balance sheet and income statement up to date on the accrual basis of accounting. An accounting guideline which allows the readers of financial statements to assume that the company will continue on long enough to carry out its objectives and commitments. In other words, the accountants believe that the company will not liquidate in the near future. This assumption also provides some justification for accountants to follow the cost principle. The balance sheet reports the assets, liabilities, and owner’s (stockholders’) equity at a specific point in time, such as December 31.
- For example, machinery or equipment purchased would be noted at its purchased price rather than its current price, even if the machinery is very old, and is not worth the purchased price.
- Besides, different regulatory bodies, like SEBI, also make it compulsory for companies to completely disclose the true and fair picture of their state of affairs and profitability.
- This information is used by different internal and external users of the organization for various purposes regularly.
- Similarly, suppose the company has incurred an expense on the marketing of the firm or its products.
Our https://www.bookstime.com/ goal is to help everyone, regardless of their background or financial knowledge, gain the confidence and skills to make informed financial decisions and achieve financial success. Money Instructor® provides comprehensive resources that empower young people and adults with practical knowledge and skills in money management, investing, business, and the economy. Our resources include engaging lesson plans, interactive lessons, worksheets, informative articles, and more. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) hasworked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. A decrease in the value of a long term asset to an amount that is less than the amount shown under the cost principle.
For financial statements to be relevant they should be distributed as soon as possible after the end of the accounting period. However, changes in accounting practices are permitted when justified by better information or new standards. For instance, a company might switch from the First-In, First-Out (FIFO) to the Last-In, First-Out (LIFO) inventory valuation method if it better reflects economic conditions.
- When the revenues are earned they will be moved from the balance sheet account to revenues on the income statement.
- These are as common to accountants in their work as the air is around us.
- This principle often requires judgments, such as estimating warranty expenses at the time of sale to align them with revenue, even if the actual costs are incurred later.
- While GAAP and IFRS have differences, they share the same core goal that emerged from the 1930s reforms—protecting investors through transparency and consistency.
- Some of the accounting principles in the Accounting Research Bulletins remain in effect today and are included in the Accounting Standards Codification.
Liabilities and owner’s equity go on the right side of the equation and are credited. For example, if the company issues shares of common stock, your software would credit that amount to the owner’s equity account. Failure to follow this concept can make your online bookkeeping much more difficult and even land you in legal trouble if you’re a corporation or limited liability company. In those cases, you can preserve limited liability protections only by separating business and personal finances. Of course, the accountant or auditor is free to come to a different conclusion if there’s evidence that the business can’t pay back its loan or meet other obligations.

Accounting Period Concept
The company will record a land cost of $25,000 in its fundamental accounting concepts accounting records. Five years later, in a booming real estate market, the land’s fair market value may be $35,000. While the market value of the land has increased significantly, the balance sheet and other accounting records would remain unchanged at the cost of $25,000. Fees earned from providing services and the amounts of merchandise sold.